
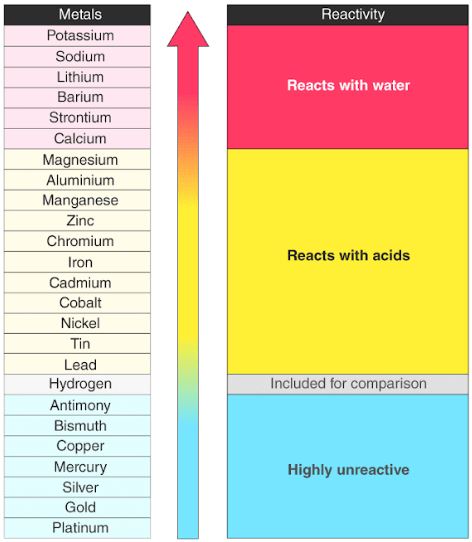
A simple form of it is shown here: sodium. The non-metals hydrogen and carbon are often included in the reactivity series. Use the results in the table to deduce an order of reactivity, starting with the most reactive metal. The reactivity series shows the list of metals starting with the most reactive at the top and the least reactive at the bottom. The table shows the results of one of these investigations. Different combinations of metal and salt solution are tested. Tin will be more reactive than copper but less.

A piece of metal is dipped into a salt solution. Learners could repeat the displacement reactions experiment and include the unknown metal and metal sulfate. The reactivity series of metals is a chart showing metals in order of decreasing reactivity. the blue colour of the solution fades as blue copper sulfate solution is replaced by colourless magnesium sulfate solutionĪ reactivity series can be deduced by carrying out several displacement reactions.For example iron oxide is reduced in a blast furnace to make. Mg(s) + CuSO 4 (aq) → MgSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s) This practice sheet covers part of Topic 4 of Chemistry Chemical Changes Its designed for both GCSE Triple Award Science (separate sciences) and Double. How are metals below carbon on the reactivity series extracted By reduction using carbon. Magnesium + copper sulfate → magnesium sulfate + copper It displaces copper from copper sulfate solution : For example, magnesium is more reactive than copper. Displacement in solutionsĪ more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its compounds.

At the same time, copper oxide is reduced because oxygen is removed from it. In this reaction, carbon is oxidised because it gains oxygen. For example:Ĭopper oxide + carbon → copper + carbon dioxide Oxygen can be removed from metal oxides in chemical reactions. Reactivity of a metal is determined by its tendency to lose electrons and form positive ions. The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metal gains oxygen. By carrying out these reactions with lots of different elements, using lots of different conditions, scientists have been able put the. For example, magnesium burns rapidly in air: Many metals react with oxygen to make metal oxides. Winning is represented by having the oxide.Oxidation, reduction and displacement reactions Reactions of metals with oxygen The top team always beats the lower teams (there are no shock results!). Think of it like the football league tables. 0620 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Specimen Papers. If you are told that Blobbium is below iron in the reactivity series, then B is right. Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry past and specimen paper questions and answers. If you are told that Blobbium is above iron in the reactivity series, then A is right. It looks OK but what about this one? blobbium oxide + iron gives blobbium + iron oxide (B)īoth COULD be OK but which one really happens? You cannot tell until you know the position of blobbium in the reactivity series. The Reactivity Series helps us to predict the outcome of some reactions.ĭoes this reaction proceed? blobbium + iron oxide gives blobbium oxide + iron (A)

Reactivity series chemistry gcse free#
The profit from every pack is reinvested into making free content on MME, which benefits millions of learners across the country. The MME Chemistry cards cover all the major topics areas within the AQA GCSE Chemistry specification. We can also add in some non-metals (hydrogen goes between iron and copper carbon goes between magnesium and iron). GCSE Chemistry revision cards are the perfect revision tool to help You improve your grade. We can add in other metals but this is good enough for now. This lesson bundle covers the content for the AQA GCSE Chemistry C5. The reactivity series shows the list of metals starting with the most reactive at the top and the least reactive at the bottom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
